Legacy Functions
Introduction
UBC 1.32 introduces a new processing mode for UBC.io interfaces: the use of classes instead of function modules with macros.
UBC.io is fully backward compatible, meaning all features described in the general UBC.io documentation are also supported with function modules. To keep the documentation clear, the delta customizing and implementation for interfaces using function modules are described here. Please make sure to read the general UBC.io documentation first.
The configuration is generally the same; the only difference is that if classes are activated for the system, classes are entered instead of function modules in various places during customizing. Additionally, some implementation considerations must be respected when using function modules.
UBC.io can handle both classes and function modules in parallel. For new interfaces, consider switching to classes instead of functions (contact the metalsXP team).
Customizing
Functions
Function Name
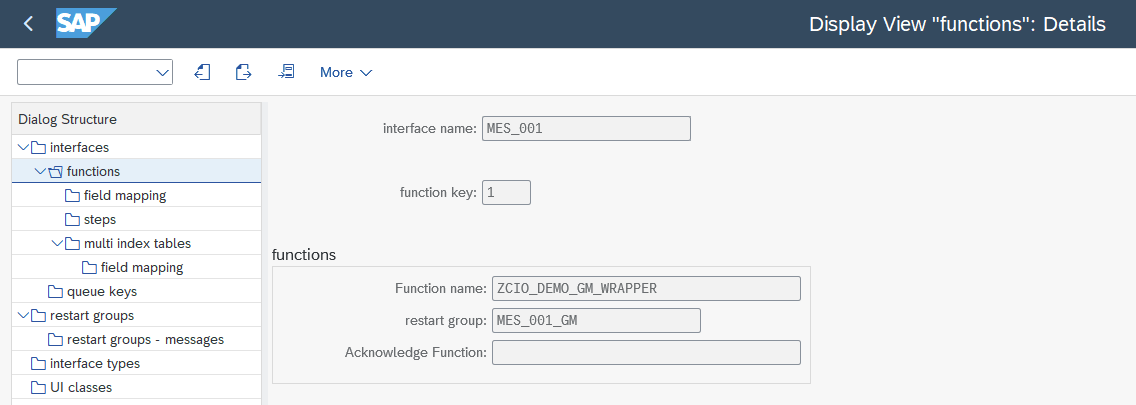
Specify a function module name as a top-level entry for the assignment to an interface. Please note that the function module must include simple calls at the beginning and end to be ready for use within UBC.io (see also Implementation).
Field Mapping
If function modules are used, the messages table (from which the message status is derived and the application log is populated) must be defined in addition to the field mappings.
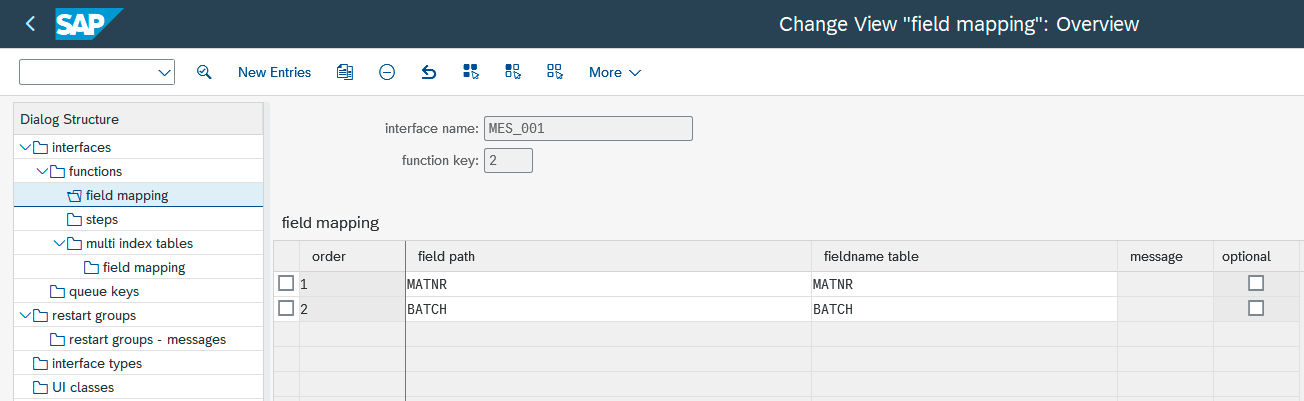
Define the path to the messages table (e.g., ET_RETURN) and ensure the "contains messages" option is selected.
Acknowledge Function
Here, you may optionally assign a function module name to be triggered when a message is acknowledged. The function module must have exactly the same signature (1:1) as the function specified in Function Name. It should only contain logic, with no additional begin and end macro calls.
Multi-Step Function
In a multi-step scenario, a list of function modules must be assigned here.
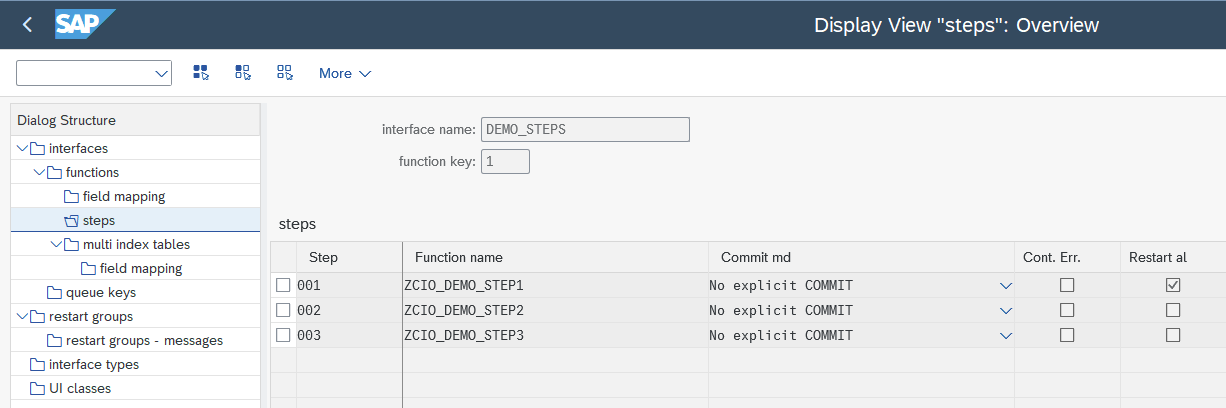
In this scenario, the top-level function module entered in the Functions section acts only as a wrapper and/or session initialization module. The function module must have exactly the same signature (1:1) as the function in Function Name and contain only logic, with no additional begin and end macro calls.
See implementation details in Multi-Step Interfaces.
Implementation
Triggering Interfaces (Top-Level Function Module Only)
- The Customizing must be completed for your top-level function module.
If multiple steps are used, you are free to define the relation through customizing. - Your top-level function module must be called like any other function module in your code. Ensure that a
COMMIT WORKis included at the end of your program to trigger interface persistence. - Include
/UBC/IO_MACROSin your function group/module. - The first statement in the function module must be
_ubc_io_begin ''.warningThe function module will exit immediately if not called by the framework and is asynchronous. The exporting parameters will remain empty.
- The last statement in the function module must be
_ubc_io_end ''.
Logging will be completed automatically by the framework. - Ensure there are no explicit commits within your function module. Commit and rollback are controlled by the framework: an automatic commit is executed if successful, and a rollback if not.
AvoidCOMMIT WORK, which would interfere with auto-restartability. If technically required (e.g., when posting multiple goods movements), consider using the Multi-Step Approach.
The rest of your function module can remain unchanged!
Example:
function /ubc/io_template_fm_single
importing
iv_matnr type matnr
iv_werks type werks_d
exporting
et_return type bapiret2_t
raising
/c09/cx_cio_persistency.
"include UBC.io macros
include /ubc/io_macros.
"clear exporting variables
clear et_return.
"UBC.io: begin
_ubc_io_begin ''.
"#TODO: actual implementation goes here, please make sure to embed the logic between "begin" and "end"
"make sure end will be called in any case, thus do not use e.g. RETURN statement
"if iv_matnr = '4711'.
"endif.
"UBC.io: finish
_ubc_io_end ''.
endfunction.
And the actuall call:
call function '/UBC/IO_TEMPLATE_FM_SINGLE'
exporting
iv_matnr = '4711'
iv_werks = '123'.
commit work.
Multi-Step Interfaces
- The top-level function module specified in Functions must adhere to the previously described contract; see Triggering Interfaces.
- Every "Step Function Module" must not include any macros. It is controlled by the top-level function module (begin and end) and should only contain business logic.
- The top-level function module may optionally include initialization routines between the "begin" and "end" macros.
- Ensure that your Step Function Module does not contain any
COMMIT WORKorROLLBACK WORK, as this would break auto-restartability. - Your Step Function Module must have exactly the same function module signature as your top-level function module.
If you need to exchange information between steps, consider using an optional changing parameter (add it to all involved function modules).
The parameters will be passed to the next function.
Templates
To speed up development, ABAP templates are available for single functions and functions with multiple steps/LUWs.
See package /UBC/IO_TEMPLATE_LEGACY.